Linear Plot: A Simple 5-Step Framework
Hello Writers, Linear plot is one of the popular plots which is highly used in novels, movies and dramas. And today we will understand Linear Plot in detail. But before delving into that particular part we have to build an understanding for plot and it’s not wrong if I say plot is the root of any story. If the root is strong then the story automatically puts a stronger impact on the reader’s minds and hearts!
Now, When we hear the word plot, it immediately brings to our mind, a series of events that unfold in a story. Whether it’s a novel, movie, or even a short story, the plot is the backbone that holds the narrative together. A well-crafted plot has the power to grab readers or viewers and immerse them in the storyline. One type of plot that is frequently used, especially in straightforward storytelling, is the linear plot obviously! As we discussed! But what does it mean? How do we create one, and what makes a plot engaging? Let’s dive into the answers step by step!
WHAT IS A PLOT?
Let’s first define the term plot in simple words. A plot is the sequence of events that form the structure of a story. For better understanding let’s have an example! Have you seen a jigsaw puzzle! Haha! Are you kidding! So this is the very thought you are having right now! But wait, wait, because today we try to see the jigsaw puzzle from the writer’s perspective!
So, let’s assume that each puzzle of a Jigsaw is a plot! Because if you miss a single puzzle the final picture would be incomplete! Now ask yourself, Why?
Now, You got your answer! Yes, because every puzzle is connected to some other puzzle directly and indirectly! Every puzzle has its own meaning and if you place it one by one it would complete the whole picture with meaning!
So, Plot does the same for a story, if you arrange it event by event then it transforms the story completely and meaningfully!
Remember the stronger the plot then the stronger, impactful and meaningful the story becomes!
NOW LET’S DISCUSS THE IMPORTANT PARTS OF ANY PLOT
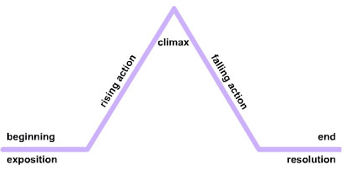
Beginning (Exposition): Where the story introduces the characters, setting, and initial conflict.
Middle (Rising Action, Climax): The events that escalate the conflict and lead to the turning point.
End (Falling Action, Resolution): Where the conflict is resolved, and the story comes to a conclusion.
A PLOT ESSENTIALLY ANSWERS THE QUESTION: What happens in the story? Without a clear plot, the story might seem chaotic or lack direction.
TYPES OF PLOT
While there are numerous ways to tell a story, the following are the most common types of plots:
LINEAR PLOT: The events occur in chronological order. The story flows from the beginning to the end without jumping back and forth in time. (More on this below!)
NON-LINEAR PLOT: The story events are not told in order. It may include flashbacks, time jumps, or parallel timelines.
CIRCULAR PLOT: The story begins and ends at the same point, giving it a cyclical structure.
EPISODIC PLOT: The story is broken into separate, self-contained episodes that are loosely connected.
PARALLEL PLOT: Multiple storylines unfold side by side and may intersect at certain points.
Here you can check how you can improve your writing style.
For now, let’s focus on LINEAR PLOT, which is the simplest and most commonly used structure in storytelling.
WHAT IS A LINEAR PLOT?
A linear plot follows a straightforward, chronological sequence of events. It begins at point A (introduction), proceeds to point B (conflict and rising action), and eventually reaches to point C (resolution).
THINK OF IT LIKE A STRAIGHT LINE:
Start → Conflict → Climax → Resolution
For example, in a classic fairy tale like Cinderella, the plot moves in a clear sequence:
Introduction: Cinderella lives with her wicked stepmother and stepsisters.
Rising Action: She wants to go to the royal ball but faces obstacles.
Climax: She attends the ball with the help of the fairy godmother.
Falling Action: The prince searches for the owner of the lost glass slipper.
Resolution: Cinderella fits the slipper, marries the prince, and lives happily ever after.
In short, the events happen in the exact order they occur in time.
SOME MORE EXAMPLE OF A LINEAR PLOT IN A STORY
Let’s look at a detailed example of a linear plot in a well-known story: Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone.
Exposition: Harry lives with the Dursleys and learns he is a wizard.
Rising Action: He goes to Hogwarts, makes friends, and begins to unravel the mystery of the Sorcerer’s Stone.
Climax: Harry confronts Professor Quirrell and Voldemort to prevent them from stealing the Stone.
Falling Action: The danger passes, and Harry is praised for his bravery.
Resolution: Harry returns to the Dursleys for the summer, knowing he has a place at Hogwarts
The story unfolds in a natural, chronological sequence that makes it easy to understand while building excitement as Harry’s challenges increase.
WHY IS A LINEAR PLOT EFFECTIVE?
Easy to Follow: A linear plot is clear and simple, making it ideal for readers and viewers who want a straightforward story.
Natural Flow: It mimics the way events occur in real life, creating a sense of realism.
Focus on Conflict: Without time jumps or flashbacks, the story keeps its focus on the conflict and its resolution.
Great for Beginners: Writers who are new to storytelling often start with linear plots because they are easier to structure.
LINEAR PLOT IN DIFFERENT MEDIA
Novels: Many novels, such as The Old Man and the Sea: (1952) by Ernest Hemingway and Pride and Prejudice: (1813) by Jane Austen follow a linear plot. The events are narrated in the order they happen.


Movies: Classic films like Titanic and The Shawshank Redemption use linear plots to keep the audience engaged.


Short Stories: Simple stories like fairy tales or fables often follow linear plots because of their clear and concise structure.


KEY POINTS TO REMEMBER WHILE CREATING A LINEAR PLOT
Follow Chronological Order: Ensure the events occur in a logical, time-based sequence. Avoid flashbacks or time jumps.
Build a Clear Conflict: A strong conflict drives the story forward and keeps readers engaged.
Use Cause and Effect: Every event in the plot should have a reason and consequence that leads to the next event.
Maintain a Natural Flow: Avoid unnecessary subplots that distract from the main storyline.
Focus on Character Development: Make sure your protagonist evolves through the story’s events.
Create a Satisfying Climax: The turning point should feel rewarding and resolve the story’s main conflict.
Tie Up Loose Ends: Provide a clear and satisfying resolution that gives the audience closure.
I think until now, you have got a better understanding of the plot but here comes one more critical question that the writer finds very difficult and the question is “what is the difference between plot and the story?”
Most of the writers get easily confused here, they often think while brainstorming that is I building a story or a plot? What do I do first? What is the difference between story and plot?
Some very complicated and confusing questions arrive in their mind! So, to resolve it we will discuss it also! Because it is very essential for a writer to understand otherwise it would be problematic for you!
And don’t worry, believe me it’s not that difficult to understand! For now, without any delay let’s dive into the very section of story and plot!

The terms plot and story are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different elements of a narrative. Understanding their distinction can enhance both writing and analysis of literature, films, or any narrative art form.
STORY refers to the what of a narrative—the sequence of events in chronological order. It focuses on the core content: who did what, where, and when. A story gives us the raw material of a narrative without emphasizing causality or structure.
PLOT, on the other hand, refers to the how of a narrative—the structured arrangement of events presented to the audience. It emphasizes cause and effect and can manipulate the order of events to create suspense, drama, or emotional impact. Let’s try to understand it more clearly with some examples:
Example 1:
In the story of “The King died, and then the queen died”, we simply have a sequence of events. This is the story.
The plot could be structured as: “The king died. The queen, stricken with grief, could not bear the loss and died of heartbreak.” Here, the plot adds causality, linking events to create meaning and emotional depth.
Example 2:
In “Romeo and Juliet” by Shakespeare:
Story: Two young lovers from feuding families fall in love and die tragically.
Plot: The events are presented with a dramatic arc—Romeo and Juliet meet, secretly marry, face misunderstandings, and eventually take their own lives due to miscommunication. The arrangement of scenes, revelations, and character decisions drives the tragedy.
SUMMARY
While the story is the raw sequence of events, the plot structures those events to add causality, tension, and emotional resonance. A strong plot transforms a simple story into a compelling narrative.
Now let’s try to learn how to develop exciting plots:
HOW TO DEVELOP A PLOT
Now that we understand what a plot is, let’s talk about how to develop one. Whether you’re writing a novel, short story, or movie script, follow these simple steps:
1. Start with an Idea
All stories begin with an idea. Ask yourself:
What story do I want to tell?
Who are the main characters?
What is the main conflict or challenge?
2. Create a Structure
A strong plot needs structure. Use the 5 essential elements:
Exposition: Set the stage with characters and setting.
Rising Action: Introduce the conflict and build tension.
Climax: The turning point where the conflict reaches its peak.
Falling Action: Events begin to wrap up.
Resolution: The conflict is resolved, and the story concludes.
3. Add Conflict
Conflict is the heart of any story. It could be:
Character vs. Character (e.g., Harry Potter vs. Voldemort)
Character vs. Nature (e.g., The Martian by Andy Weir) (Mark vs. Mars planet)
Character vs. Society (e.g., The Hunger Games)(Human vs. Society)
4. Create Engaging Characters
Your audience needs characters they can connect with. Develop your characters’ goals, motivations, and flaws.
5. Write a Clear Ending
A satisfying ending gives closure to the audience. Make sure it ties up all loose ends.
HOW TO MAKE A PLOT DIAGRAM
It may be helpful for you while creating a story. A plot diagram is a visual representation of a story’s structure. It’s a simple tool to map out the sequence of events. Here’s how to create one:
Draw a Triangle or Pyramid: This represents the rising and falling action of the story.
Label the following points:
Exposition: Bottom left (introduction of characters and setting).
Rising Action: The upward slope (events building to the climax).
Climax: The peak of the triangle (turning point).
Falling Action: The downward slope (events leading to the resolution).
Resolution: Bottom right (conclusion).
A plot diagram helps you organize your ideas and ensure your story flows naturally.
WHAT IS THE PLOT OF A STORY?
We have discussed plot, types of plots, Difference between story and plot. Now we are going to discuss the plot of a story! It is the sequence of events that drive the narrative forward. It’s the answer to what happens in the story. A good plot keeps readers engaged and curious about what happens next.
For example:
In The Lion King, the plot follows Simba’s journey from a carefree cub to a wise king.
In The Great Gatsby, the plot revolves around Gatsby’s love for Daisy and his ultimate downfall.
HOW TO WRITE A PLOT OF A STORY
Here are a few simple tips to write an engaging plot:
Know Your Audience: What type of story will they enjoy?
Outline Your Plot: Use the 5 elements of a plot to create a basic structure.
Focus on Conflict: The tension or struggle keeps readers hooked.
Make Every Scene Count: Each event should move the story forward.
End with a Bang: A strong ending leaves a lasting impression.
PLOT IN MOVIES
A good plot is essential for a successful movie. Take Titanic, for example:
Exposition: Jack and Rose meet on the Titanic.
Rising Action: Their love story develops amid social class differences.
Climax: The ship hits an iceberg.
Falling Action: Passengers struggle to survive.
Resolution: Jack sacrifices himself for Rose.
This linear plot creates an emotional and engaging experience for the audience.
PLOT TWISTS IN MOVIES
A plot twist is an unexpected turn of events that surprises the audience. Some of the best movies are remembered for their shocking twists.
Examples of Famous Plot Twists:
The Sixth Sense: “I see dead people.” The twist reveals that Dr. Crowe is dead.
Fight Club: The narrator and Tyler Durden are the same person.
The Prestige: The shocking secret behind the magician’s trick.
Plot twists make the story more unpredictable and exciting.
Some Movies and Novels with the Best Plot Twists
Here are a few movies and novels that feature brilliant plot twists:
Movies:
Toy Story
Novels:
Orphans: By Charles D’Ambrosio
The Trial: By Franz Kafka
1984 by George Orwell.
These stories prove that a well-executed plot twist can make a story unforgettable.
FINAL THOUGHTS ON LINEAR PLOT
A linear plot is a straightforward storytelling structure where events unfold in chronological order, guiding the audience through a clear beginning, middle, and end. This simplicity allows for direct engagement with the narrative, making it an ideal choice for stories focused on character growth, conflict resolution, or a specific message. By adhering to this structure, writers can create a cohesive and accessible experience for their audience, ensuring that the progression of events feels natural and easy to follow.
However, while linear plots offer clarity, they may risk predictability if not carefully crafted. To maintain interest, writers should focus on building compelling characters, introducing meaningful stakes, and layering subplots or thematic depth within the sequence. A well-executed linear plot doesn’t just recount events—it weaves them together to form an emotionally resonant and satisfying story.
Ultimately, a linear plot serves as the backbone of many great narratives, proving that simplicity in structure can be a powerful tool when paired with creativity and purpose.


